The strategy to classify, affect, and control diseases transmitted from animals to humans
Humans, animals, and
the environment play an important role in the development and transfer of
diseases arising from different types of germs. Many pathogen-caused diseases
in humans are also found in animals. According to the World Health
Organization, zoonotic diseases refer to a disease that transmits from humans
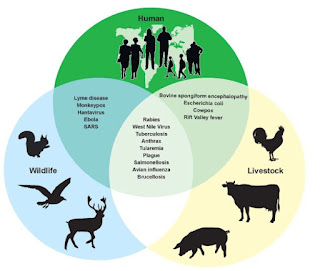
to animals or from animals to humans. There are 13 major diseases transmitted
from animals to humans in developing countries of the world, which affect
farmers in different ways. These diseases make four billion people sick
annually and kill 2.7 million people, while also reducing animal production.
Classification
of diseases transmitted from animals to humans
Diseases transmitted
from animals to humans are caused by a variety of pathogens. Because of their
etiology, these diseases are classified into many categories. At first level, there are diseases transmitted
from animals to humans that are caused by a variety of bacteria (e.g. anthrax,
salmonella, TB, brucellosis). In the second level, there are diseases
transmitted from animals to humans that are caused by a variety of viruses (rabies,
ebola, avian influenza), in the third grade, diseases caused by a variety of
parasites (trichomonosis, toxoplasmosis, tremattodosis, malaria, echinococosis). The fourth is disease that arise from
ringworm.
Diseases
transmitted from domestic animals to humans
Domestic animals play
an important role in transmitting diseases to humans. Cows, buffaloes, sheep,
goats, horses, and cats have a variety of pathogens that can be transmitted to
humans and cause various diseases. These diseases are transmitted to humans in
different ways. Some diseases are transmitted by touching animals, while there
are some diseases whose pathogens are released into the air by animals, and
when humans breathe in that air, the disease is transmitted. However, there are
some diseases that are transmitted by animal bites. The diseases transmitted
from animals to humans include anthrax, salmonella, TB, brucellosis, rabies,
ebola, avian influenza, tricogenesis, toxoplasmosis, trematodosis, malaria, and
echinococosis, which are of greater importance.
Anthrax is very important
among diseases transmitted from animals to humans. The pathogen of this disease
survive for a very long time in the soil and are prone to spreading the
disease. This disease is transmitted to humans when humans and animals such as
sheep, goats, and cows are kept in one place. In addition, the disease can be
transmitted from one person to another. Globally, about 2,000 to 20,000 people
are affected by the disease each year. The mortality rate from this disease
ranges from 25 to 65% in countries whose economies depend on agriculture, where
the disease is causing a lot of losses.
The other major disease
which is transmitted from animals to humans is known as tuberculosis or TB. It
is the cause of a great decline in animal production. This disease is caused by
the bacteria Mycobacterium bovis. The
disease can be spread to humans through animal cough, and it can also be passed
through animal milk if it is not boiled and utilized. Many people working with
animals, such as veterinary doctors, butchers, and others, are very prone to
disease from the affected animal, so every effort should be made to prevent the
disease.
Brucellosis is one of
the most common disease transmitted from animals to humans, affecting roughly
500,000 people worldwide each year. This disease is caused by Brucella bacteria. The disease can be
transmitted to humans by contaminated air and un-boiled animal. In addition,
animals are aborted, lameness is prevalent, and milk produced by the animals
decreases. The condition affects those who work on dairy farms, veterinary
professionals, and other workers. This poses a greater risk, so brucellosis
should be tested on the farm, and the affected animals should be separated.
Rabies, also known as
bawala pan, is another important disease spread by animals to humans. Rabies
kills 20,000 to 70,000 individuals per year throughout the world. The germs
that cause this disease are more common and are found in cats, and from these
animals it is transmitted to humans. In developing countries, the disease is
also transmitted by dog bites. The appearance of the disease in humans depends
on the place where the affected animal has bitten. The obvious signs of the
disease are that the animal affected by it is very afraid of water.
Diseases
transmitted from pets and birds to humans
The risk of diseases
being transmitted from pets to humans has considerably increased as a result of
human-pet friendship. About 14 to 62% of people keep their pets in their
bedrooms, which has increased the risk of these animals transmitting diseases
to humans. More serious infections include Brucellosis, Campylobacteriosis,
Rabies, Influenza, Q-fever, Hookworm, Salmonellosis, and Toxoplasmosis. Nowadays, the practice of keeping birds of
different species in homes has also become very popular. These birds, including
gravel parrots, Australian parrots, and other different birds, transmit various
diseases to humans. Avian chlamydiosis, avian influenza, and salmonellosis are
more important in diseases transmitted from birds to humans.
Effects
of diseases transmitted from animals to humans
Although it is a
difficult task to assess the effects of disease transmitted from animals to
humans, we can generally see the number of people affected by the disease and
its effects due to problems arising from the disease. Diseases transmitted from
animals to humans have serious consequences for humans, such as causing people
to perform their regular jobs incorrectly. It is a major problem, especially in
developing countries. There are some diseases in which a person has to be
separated from other human beings. In such a situation, these diseases also
cause mental illness. If animals die from diseases transmitted from animals to
humans, they have a very negative effect on livestock farmers, and if these
animals are only affected by the disease and do not die, they greatly reduce
production, so that the farmer faces a lot of problems economically. Production
decreases by a percentage. The loss in human milk supply, the reduction in meat
supply, and the reduction in wool and egg supply all reflect this decline. Similarly,
some disorders render animals sterile indefinitely, preventing them from having
calves in the future. This significantly reduces the profits of dairy farms.
Some diseases, such as anthrax and avian influenza, cannot be transferred from
one country to another, thus causing various problems in global trade. Due to
the mad cow disease in animals, there has been a great decline in animal trade
globally, as a result of which many countries have suffered economically. There
are some diseases that are very prominent in developing countries, such as the
problems of declining production from animals suffering from the disease of
brucellosis.
Ways
to control diseases transmitted from animals to humans
Since the diseases transmitted from animals to
humans are interrelated among man, animals and the environment, we need a
multidimensional approach to control these diseases. Surveillance is of great
importance in controlling such diseases. With the help of surveillance, we can
detect the disease at the beginning, so the infected humans and animals can be
thoroughly researched, and with the help of surveillance, we can take various
steps to control the disease in time. Surveillance is critical in various
regions around the world since diseases carried from animals to humans are
prevalent everywhere. The best labs and more manpower are required for a
successful surveillance program. To control diseases transmitted from animals
to humans, we can conduct the four surveillance activities listed below:
• Pathogen surveillance,
which indicates the disease-causing pathogens
• Serological surveillance,
in which pathogens are checked in blood samples of humans and animals
• Syndrome
surveillance, this procedure collects records of humans and animals suffering
from disease and then concludes with the help of this record
• Risk surveillance,
which examines various factors that cause disease.
To control these
diseases, we can also use various other methods, such as providing treatment to
affected animals, vaccination of healthy animals, reducing animal movement in
various places, and removing affected animals from the herd. The disposal of
animals affected by the disease can also control various diseases. In the case
of diseases that are transmitted by touching the affected animal, the items
used by the animal should be handled carefully.
There are some diseases
that affect animals more than once. We must adopt a comprehensive strategy to
control such diseases that can affect us more often. There are some diseases
transmitted from animals to humans that we can completely eradicate with a
comprehensive strategy, but there are many problems in developing countries
with eradicating them. To prevent diseases that are transmitted from animals to
humans, we must implement a One Health strategy in which medical doctors, veterinary
doctors, and other health professionals collaborate to solve these problems.
We also have to make
various laws to control diseases transmitted from animals to humans and
implement them strictly, as when animals are brought from another country to
our country, first they should be kept in a protective place for a period of
time and tests should be conducted on various diseases found in them. We can
also control these problems because of the vaccination program, creating
awareness among individuals so that they are aware that these diseases are
transmitted to humans and cause various problems.
For more guidance and consultancy feel free to reach out to me. I'd be happy to assist you.







2 Comments
I am really thankful to you for this content and informative details. I really like your blog and content about Merino Sheeps For Sale topic. I truly appreciate your work and efforts. well done.
ReplyDeleteThis blog post provides a comprehensive overview of zoonotic diseases and their impact.
ReplyDelete